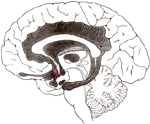
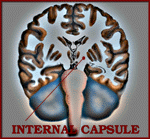
Brain Structure |
Function |
Associated Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
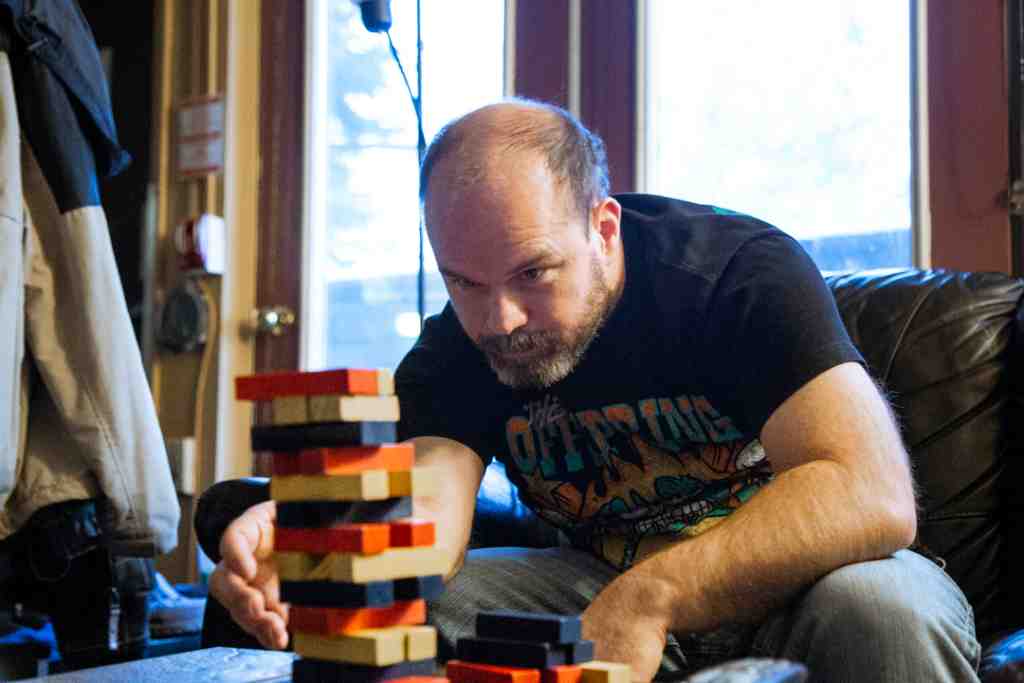
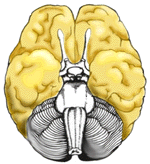
Cerebral Cortex
Ventral View |
The outermost layer of the cerebral hemisphere which is composed of gray matter. Cortices are asymmetrical. Both hemispheres are able to analyze sensory data, perform memory functions, learn new information, form thoughts and make decisions. | |
Left Hemisphere
|
Sequential Analysis: systematic, logical interpretation of information. Interpretation and production of symbolic information:language, mathematics, abstraction and reasoning. Memory stored in a language format. | |
Right Hemisphere
|
Holistic Functioning: processing multi-sensory input simultaneously to provide "holistic" picture of one's environment. Visual spatial skills. Holistic functions such as dancing and gymnastics are coordinated by the right hemisphere. Memory is stored in auditory, visual and spatial modalities. | |
Corpus Callosum
|
Connects right and left hemisphere to allow for communication between the hemispheres. Forms roof of the lateral and third ventricles. |
|
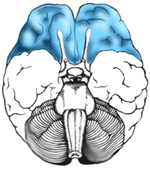
Frontal Lobe
Ventral View
Side View |
Cognition and memory. Prefrontal area: The ability to concentrate and attend, elaboration of thought. The "Gatekeeper"; (judgment, inhibition). Personality and emotional traits. Movement: Motor Cortex (Brodman's): voluntary motor activity. Premotor Cortex: storage of motor patterns and voluntary activities. Language: motor speech |
|
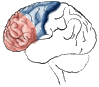
Parietal Lobe
|
Processing of sensory input, sensory discrimination. Body orientation. Primary/ secondary somatic area. |
|
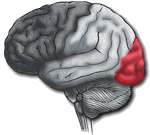
Occipital Lobe
|
Primary visual reception area. Primary visual association area: Allows for visual interpretation. |
|
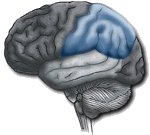
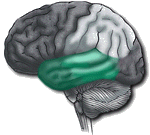
Temporal Lobe
|
Auditory receptive area and association areas. Expressed behavior. Language: Receptive speech. Memory: Information retrieval. |
|
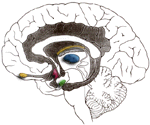
Limbic System
|
Olfactory pathways: Amygdala and their different pathways. Hippocampi and their different pathways. Limbic lobes: Sex, rage, fear; emotions. Integration of recent memory, biological rhythms. Hypothalamus. |
|
Basal Ganglia
|
Subcortical gray matter nuclei. Processing link between thalamus and motor cortex. Initiation and direction of voluntary movement. Balance (inhibitory), Postural reflexes. Part of extrapyramidal system: regulation of automatic movement. |
|
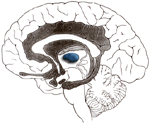
Thalamus
|
Processing center of the cerebral cortex. Coordinates and regulates all functional activity of the cortex via the integration of the afferent input to the cortex (except olfaction). Contributes to affectual expression. |
|
Hypothalamus
|
Integration center of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Regulation of body temperature and endocrine function. Anterior Hypothalamus: parasympathetic activity (maintenance function). Posterior Hypothalamus: sympathetic activity ("Fight" or "Flight", stress response. Behavioral patterns: Physical expression of behavior. Appestat: Feeding center. Pleasure center. |
|
Internal Capsule
|
Motor tracts. |
|
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
|
Responsible for arousal from sleep, wakefulness, attention. |
|
DEFINITION OF ABI
Developed by the Clinical Data Working Group of the Toronto ABI Network and adopted by their Advisory Committee
TYPES OF HEAD INJURY
Describes the different types of brain and head injuries, including the complication and recovery process.
PHYSICAL CHANGES
Describes how brain injury may lead to physical changes which can be temporary or permanent, severity and location of the brain injury.
COGNITIVE CHANGES
Describes how cognitive changes after brain injury can affect the way a person thinks, learns and remembers.
EMOTIONAL/BEHAVIOURAL CHANGES
Describes changes in a person's emotional reaction or behaviour after a brain injury, often the most difficult for the individual and families to deal with.
HORMONAL CHANGES
Describes some of the common issues as they relate to hormonal changes following an aquired or traumtic brain injury.
FUNCTION & SYMPTOMS
Describes brain anatomy, its functions and symptoms following an aquired or traumtic brain injury.
3D BRAIN INTERACTIVE
Information on disorders, brain damage, case studies, and links to modern neuroscience research.
BRAIN STIMULATION
Describes the anatomy of the brain and its function with a special interactive feature.
Ranchos Los Amigos Scale
Describes this medical scale used to assess individuals after a brain injury, based on cognitive and behavioural presentations as they emerge from coma.
STATISTICS
Download the PDF document and view the staggering true numbers - and see how it compares with other health conditions.